REU 2026 Summer Projects
List of Summer Projects
- 3D-Printed Tendon-Driven Neck Mechanism for a Vision-Based Autonomous Robot
- Optimal Control for Bio-Inspired Swimmers and Flyers
- Navigation of Microgravity Surfaces Using Tethers
- Control Optimization of a Liquid Fuel Desulfurization System
- Interactive XR-Based Digital Twin of a Robotic Manipulator
- Autonomous Visual Perception and Semantic Reasoning for Service Robots
- Automated Controls for a Rapid Testing Setup for High-Temperature Electrochemical Cells
- Soft Wearable Robotic Orthosis for Body Motion Tracking During Walking
- Averting a Mayday!: Predicting Trajectories of Bird Flocks with AI to Prevent Bird Strikes with Aircraft
Summer Project Descriptions
3D-Printed Tendon-Driven Neck Mechanism for a Vision-Based Autonomous Robot

This project explores a 3D-printed, tendon-driven robotic neck inspired by human cervical biomechanics to advance autonomous vision systems. The mechanism uses lightweight vertebra-like segments and tensioned tendons to enable smooth, multi-axis motion controlled by micro-servos. A camera paired with computer vision algorithms directs the neck’s movement, allowing autonomous tracking of visual targets. This research offers a low-cost, bio-inspired alternative to traditional rigid pan-tilt systems, potentially improving adaptability, energy efficiency, and lifelike motion in autonomous robots. By integrating biomechanics and additive manufacturing, the project supports the development of more responsive and human-like robotic platforms.
The students’ work on this project will focus on designing and prototyping the robotic system. Specific learning opportunities may include but are not limited to mechanical design skills, additive manufacturing, electronic control and sensing methods, experimental setting and data analysis approaches.
Specific skills preferred will depend on the assigned work. Mechanical design, electronic design, and robotics design are important skills. Students with experience in basic 3D printing are strongly encouraged to apply for this project in the REU program.
Optimal Control for Bio-Inspired Swimmers and Flyers

Identifying optimal swimming/flapping gaits (kinematics) is essential for designing high-performance bio-inspired robots. However, this task is challenging due to the high-dimensional parameter spaces involved, as it requires managing numerous control parameters. Traditional optimization approaches face scalability issues because the number of function evaluations (flow simulations) grows proportionally with the number of control parameters. For instance, with 1 million control parameters, 1 million flow field simulations would be required—each taking several days to complete— making such methods impractical. To overcome this limitation, we have developed an adjoint-based optimization algorithm that significantly reduces computational cost. Unlike conventional methods, this approach requires only two flow field simulations to compute the gradient, regardless of the number of control parameters. The objective of this project is to adapt and apply this adjoint-based optimization algorithm to bio-inspired swimmers/flyers, enabling the identification of their optimal gaits efficiently.
The participants involved in this project will work with state-of-the-art optimal control code and fluid dynamics simulations. The computations will be conducted on Ohio’s supercomputers.
Participants are expected to have a strong background and interest in controls, fluid dynamics, and applied mathematics. Proficiency in linear algebra and coding experience with C++ are preferred.
Navigation of Microgravity Surfaces Using Tethers

Exploration of the surfaces of asteroids will likely require a system of tethers that keep a spacecraft from bouncing into space due to low gravity. Many asteroids are simply loose piles of rubble, so tethers will need to be anchored to pitons buried under the surface rock. Robotic rovers will need to remain attached to these tethers while simultaneously traversing uneven, rocky terrain.
This student's effort on this project will involve design, modeling, and prototyping of tether-guided rovers. Primary challenges will involve remaining attached to the tether while navigating uneven terrain and obstructions of all sizes. The goal of this project will be to demonstrate tethered locomotion over actual terrain that simulates lunar or asteroid surfaces. Work effort may also include studying the use of natural materials to produce a tether in-place.
Specific skills needed will depend on the assigned work. Participants having familiarity with CAD and 3D printing is desired. Some programming experience, with application to microcontroller-operated motors is preferred.
Control Optimization of a Liquid Fuel Desulfurization System
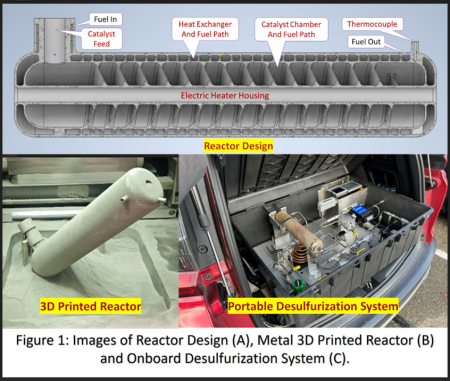
Sulfur in liquid fuels causes numerous serious problems, including emitting harmful pollutants, corroding equipment, and poisoning fuel cells. The sulfur content in JP-8 and diesel, for example, could be as high as 3000 ppmw (part per million by weight). Combustion of sulfur content fuels releases sulfur dioxide that is one of the main causes of acid rain. Fuel storage tanks, pipelines, and refining equipment suffer extremely high equipment maintenance cost because of sulfur corrosion. The U.S. Army is not able to use logistic (sulfur contained) JP-8 fuel for highly efficient fuel cell power due to sulfur poisoning fuel cell materials. The Environment Protection Agency (EPA) requires sulfur content in the ultra-low sulfur diesel (ULSD) to be 15 ppmw or less while fuel cell prefers the sulfur content 1 ppmw or less. Clearly, effectively removing sulfur from liquid fuels is imperative. Dr. Du and his team have developed a system prototype to commercialize this patented technology. The Objectives of this REU project is to Optimize the semi-auto controls into fully automatic controls of the system. The controls of the system include temperature, pressure and fuel flow rate. Outcomes from this REU project will build a path for commercialization of the technology.
The project is part of the commercialization effort of the portable desulfurization technology. The system contains hardware (metal 3D printed reactor, sorbent material, fuel inlet and outlet, thermal insulation, pump, heaters, thermocouples, tubing and valves) and software for controls. The participant will focus on the controls (temperature, pressure and fuel flow rate) of the system prototype. The student will learn how the system works with current control setup and then redesign/optimize to improve the overall control system performance. Specific learning opportunities may include but are not limited to control designs, part identification, and dynamic controls.
The participant should have basic knowledge of control systems and control design for temperature and pressure. Experience in basic electronic circuitry and electrical connections is preferred. The student is expected to contribute to the optimization of the control parameters according to the required setpoints.
Interactive XR-Based Digital Twin of a Robotic Manipulator
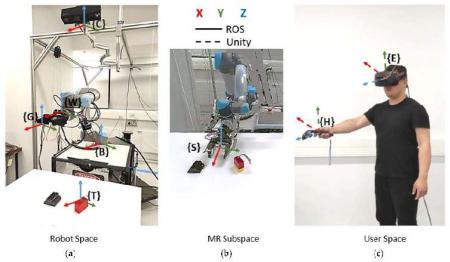
This project immerses an undergraduate researcher in the XR Lab to develop an interactive digital twin of a robotic system using virtual and augmented reality technologies. Digital twins—virtual replicas linked to real or simulated system data—are becoming essential tools for improving robotic design, monitoring, and human–machine interaction. In this project, the student will create a 3D model of a selected robot, connect it to motion or sensor data, and embed it within immersive VR/AR environments that allow users to visualize, manipulate, and evaluate robotic behavior in real time.
The project explores how extended reality can serve as a powerful interface for robotics by enabling intuitive visualization, safer testing of control strategies, and rapid iteration of design concepts. Working within the XR Lab’s multidisciplinary setting, the student will contribute to ongoing research in digital engineering and human–robot interaction by building a high-fidelity digital twin that supports analysis, training, and system development. This work advances broader efforts to integrate immersive technologies into modern engineering workflows and robotics research.
The ideal student participant will be an undergraduate majoring in mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, computer engineering, computer science, robotics, or a related field. Students should have completed foundational coursework in programming, engineering graphics, and basic systems or controls. This project is particularly well suited for students interested in robotics, extended reality (XR), digital twins, or human–machine interaction. Prior experience with VR/AR is helpful but not required.
Autonomous Visual Perception and Semantic Reasoning for Service Robots
This project develops an autonomous mobile robot capable of navigating unstructured environments through advanced visual perception and logical reasoning. Students will implement a deep learning pipeline (e.g., YOLO) to detect and classify objects in realtime.
Beyond detection, the system will utilize a symbolic reasoning module (knowledge graph) to interpret object relationships and affordances—such as distinguishing between "movable obstacles" and "static infrastructure." By integrating Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) with this high-level decision engine, the robot will autonomously plan and execute complex tasks, bridging the gap between pixel-level computer vision and cognitive robotic planning.
The ideal student participant will have an academic background in computer engineering, electrical engineering, computer science, robotics, or a closely related field. Students should have completed foundational coursework in programming, data structures, linear algebra, and basic probability or statistics. Prior exposure to robotics, artificial intelligence, or computer vision—through coursework, labs, or projects—is highly desirable but not strictly required.
The ideal student participant will have an academic background in computer engineering, electrical engineering, computer science, robotics, or a closely related field. Students should have completed foundational coursework in programming, data structures, linear algebra, and basic probability or statistics. Prior exposure to robotics, artificial intelligence, or computer vision—through coursework, labs, or projects—is highly desirable but not strictly required.
Automated Controls for a Rapid Testing Setup for High-Temperature Electrochemical Cells
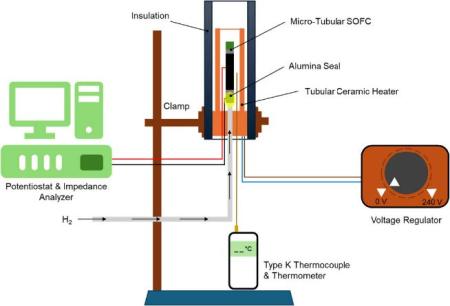
This project aims to automate a novel testing system for high-temperature fuel cells and electrolyzers. Expanding on our earlier work in developing a rapid test setup for characterizing the electrochemical performance of tubular solid oxide fuel cells, we will incorporate automated control functions and comprehensive data-logging capabilities. A key component of the design is the integration of a PID-based temperature control system, which will regulate the heating elements to maintain the electrochemical cell at the desired operating temperature, minimize fluctuations, and improve the repeatability of measurements. We will further explore the automation of the testing sequence and the switching between fuel cell and electrolyzer operating modes.
The students’ work will focus on designing and fabricating the automated control system. Specific learning opportunities may include but are not limited to mechanical design skills, electronic control and sensing techniques, and experimental data acquisition and analysis.
Specific skills will depend on the assigned work. Mechanical design and electronic design are important skills. Experience in C/C++ programming and/or PID controllers is preferred but not required. The students with experience in circuits and electronic system design are strongly encouraged to apply.
Soft Wearable Robotic Orthosis for Body Motion Tracking During Walking
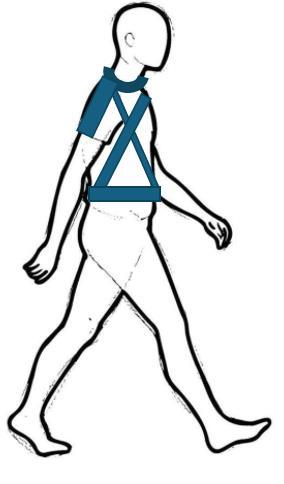
Human body motion during walking exhibits both interdependent segment movements and subtle, individualized patterns. Collecting high-quality data on the motion of different body parts is essential for understanding these correlations and personalized characteristics. However, existing tracking systems, such as rigid, full-body exoskeletons, are often bulky and inconvenient to don and doff.
This project aims to develop a compact, soft, and user-friendly wearable robotic orthosis for tracking body movements, with a particular emphasis on upper-body motion. The system is also intended to automatically identify the relationships among movements of different body segments during human walking.
The students’ work will focus on the prototype design and control for the robotic orthosis. Specific learning opportunities may include but are not limited to meta-analysis, mechanical design skills, electronic control and sensing methods, experimental setting and data analysis approaches.
Specific skills will depend on the assigned work. Mechanical design with CAD software is important. Experience in C/C++ programming is preferred. The students with experience in circuits and electronic system design are strongly encouraged to apply for this project.
Averting a Mayday!: Predicting Trajectories of Bird Flocks with AI to Prevent Bird Strikes wtih Aircraft

From 1990-2023, bird strikes in the US alone have resulted in several fatalities and injuries, a total aircraft downtime exceeding 800k hours, and costs surpassing $1B. The advent of Advanced Air Mobility, involving the use of UAVs for transportation in the low-altitude airspace, will further increase the occurrence and adverse impact of bird strikes. To address this airspace safety challenge, the goal of this project is to develop advanced physics-informed AI models to (1) identify species of bird, and (2) model and predict the short-term movement of a flock of birds, based on bird movement data. The trajectory predictions of bird flocks will then be used to plan safe and efficient flight trajectories for traditional aircraft and UAVs to prevent their collisions with birds.
Students will develop advanced AI models for bird species classification and trajectory prediction.
The ideal student will have experience with artificial intelligence / machine learning (required skill), optimization, statistics, and programming

